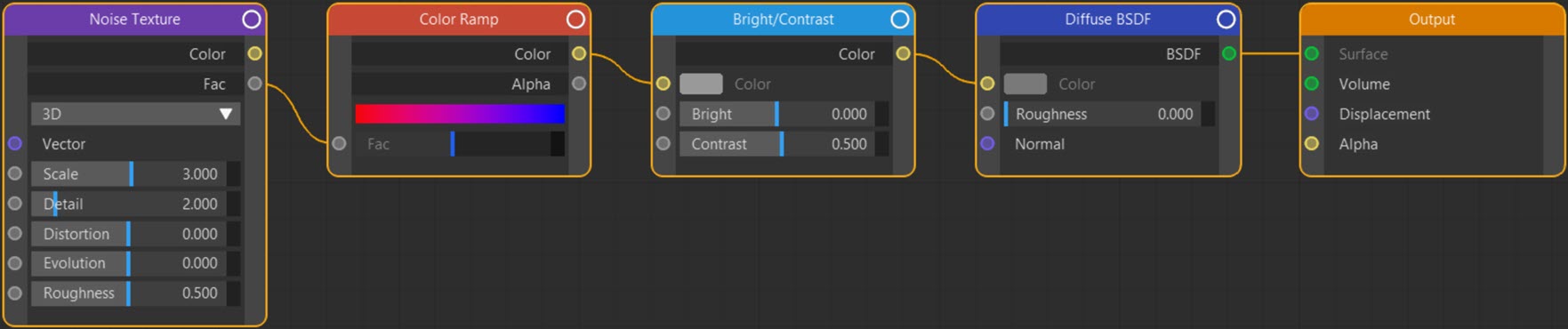
Texture: Noise
Node Interface
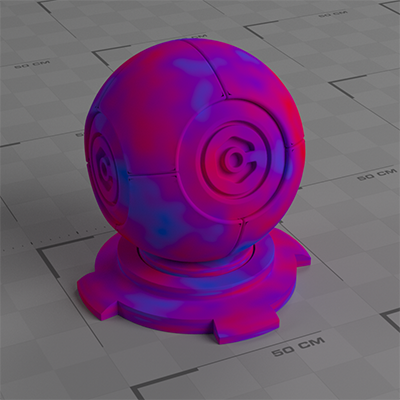
Example Output
Overview
| Function | Generates a Perlin noise |
| Nearest C4D equivalent | Noise shader |
This node produces a Perlin noise (see the Musgrave node for other noise types). By default this node produces an uninspiring, low-contrast coloured texture but manipulation of this with other nodes produces very good results.
The example above links the Fac output to a Color Ramp node then increases the contrast with a Bright/Contrast node. The node tree looks like this:
Settings
Note: a * symbol next to the name indicates the parameter also has an input port. A # symbol indicates that the parameter can only be changed with an input node, not in the node itself.
Dimensions drop-down menu
The texture is evaluated at a point in space depending on this menu. The options are:
1D
The texture is evaluated at a single point giving a uniform appearance. However, this can be changed over time by animating the 'Evolution' value.
2D
The texture is evaluated at a point in 2D space; the Z component is ignored and 'Evolution' is not used.
3D
The texture is evaluated at a point in 3D space; 'Evolution' is not used. This is the default setting.
4D
The texture is evaluated at a point in 3D space and 'Evolution' is used. That value can be animated to give an animated texture.
Vector #
The position at which the noise is evaluated. Not used if the 'Dimensions' menu is set to '1D'.
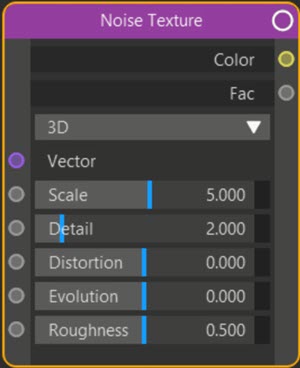
Scale *
This changes the size of the texture, but as is common in Cycles 4D, increasing the scale increases the 'amount' of texture used, so it appears smaller on the object. The effect is the same as the Musgrave node; see that page for some examples.
Detail *
Increasing this value will increase the level of detail in the noise.
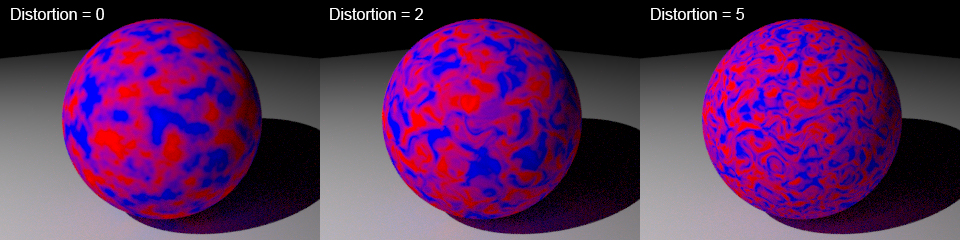
Distortion *
This setting will distort the noise giving an increasingly wavy, curly pattern:
Evolution *
Changing this value will affect the final output if the 'Dimensions' menu is set to 1D or 4D. It can be animated to produce an animated texture.
This setting in Blender is called 'W'. We have chosen 'Evolution' as a more explanatory and industry-standard name.
Roughness *
 A low value here produces a smoothly blended noise whereas a high value results in more contrast, giving a rougher, sharper noise.
A low value here produces a smoothly blended noise whereas a high value results in more contrast, giving a rougher, sharper noise.
Output
Color
A monochrome colour output.
Fac
A numeric value which is the brightness of the colour. You could link this to the Fac port of a Color Ramp node to get a coloured noise, as shown in the example at the top of the page.
Node tree