 mtSplineSample
mtSplineSample
mtSplineSample lets you resample the input spline to add Uniform, Adaptive and Distance point distribution modes. This provides even, controllable points on the spline data, making it easier to work with along the design chain.
Overview Video
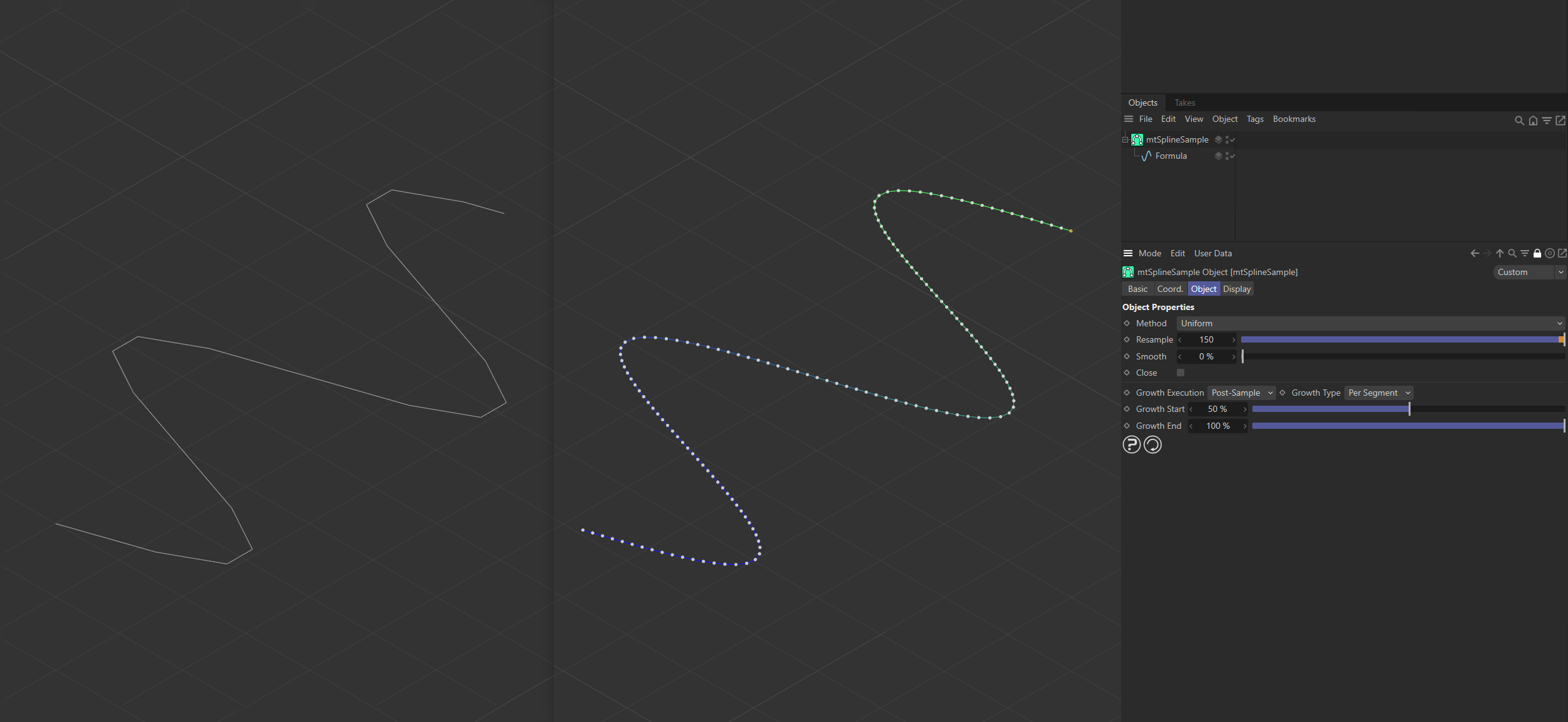
The original spline on the left has very few, unevenly distributed points. An identical spline has been placed as a child of a mtSplineSample on the right. This has been resampled using 150 points in the Uniform mode. The result is a smooth, higher-quality spline.
Object
Object Properties
Method
You have three options: Uniform, Natural and Distance.
Uniform Method
The default setting, the Uniform Method, distributes a uniform amount of points per segment.
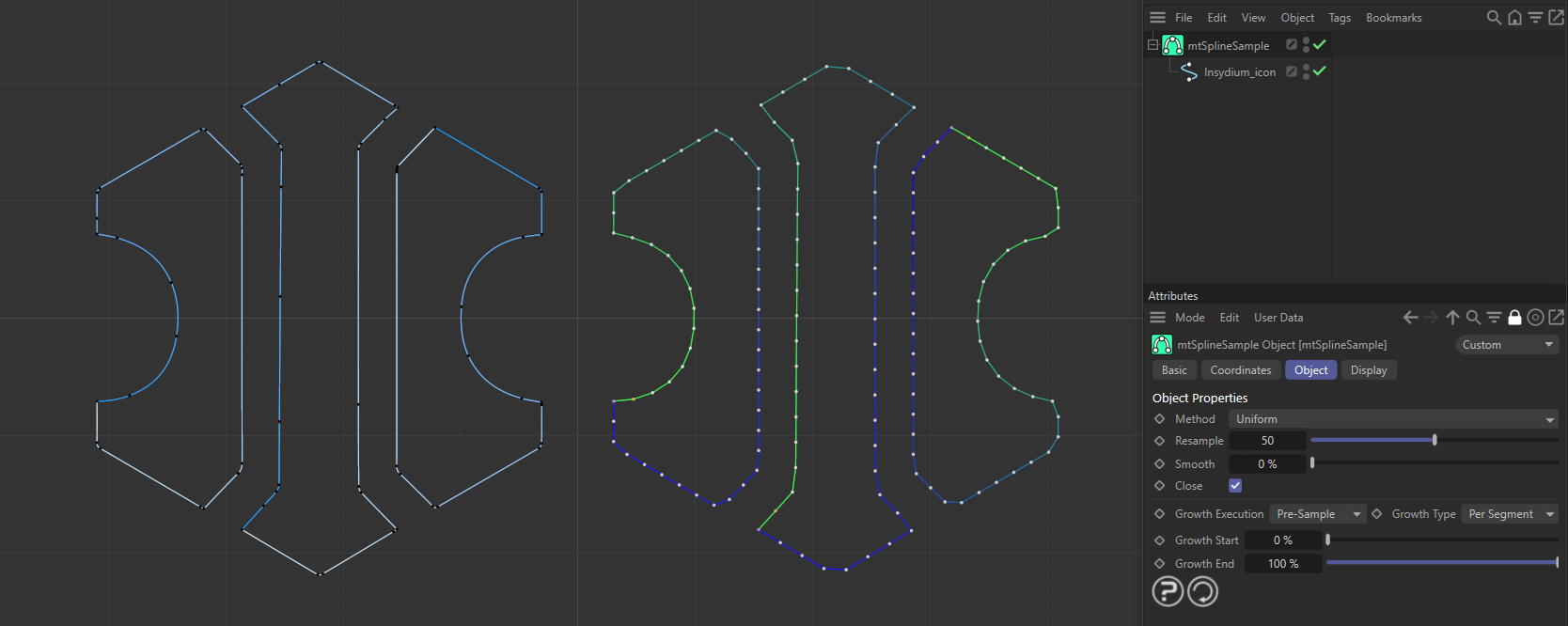
An INSYDIUM logo spline is on the left. On the right, a duplicate spline has been made a child of a mtSplineSample, using the Uniform Method.
Resample
Resample can be increased to give you a higher point count per segment.
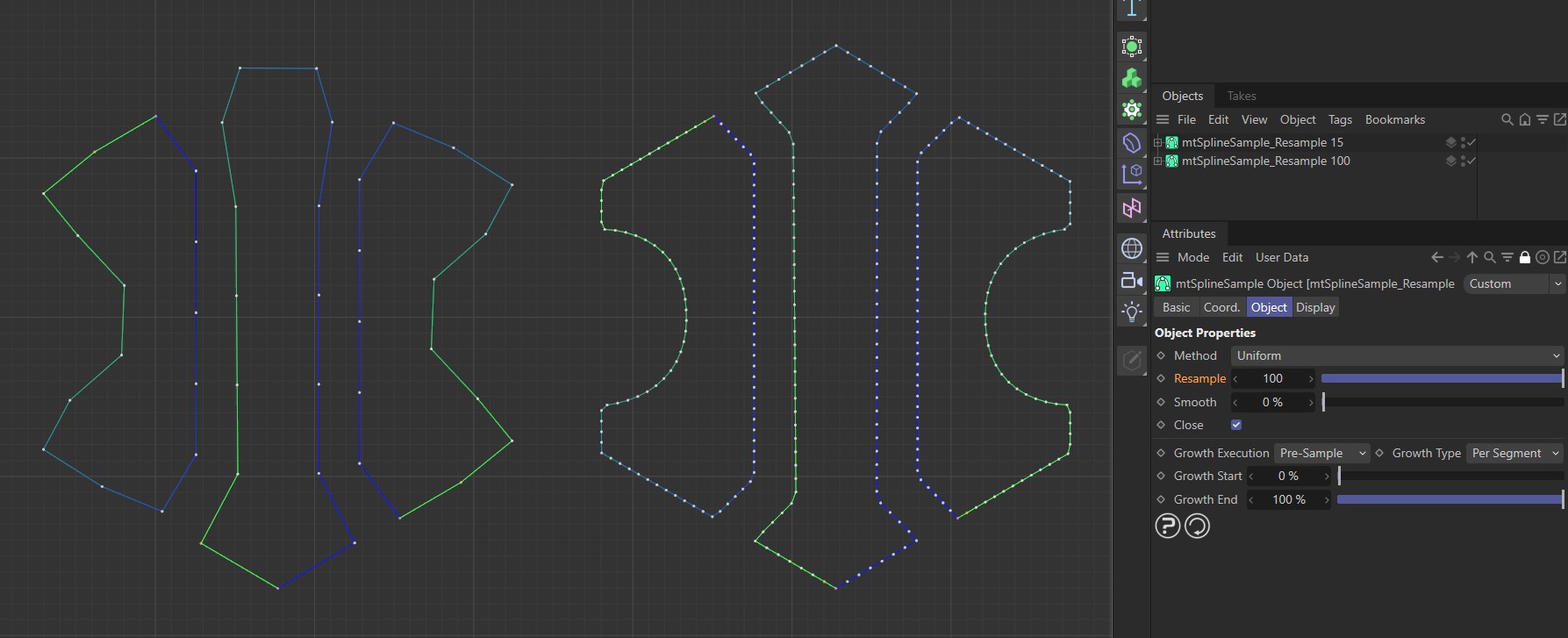
Uniform Method with a Resample value of 15 on the left and 100 on the right.
Smooth
Smooths splines on corners, by using the average point - on the segment - between neighboring points.
Animation demonstrating use of the Smooth slider.
Natural Method
Natural allocates more points where there is curvature than on straight lines of the segments.
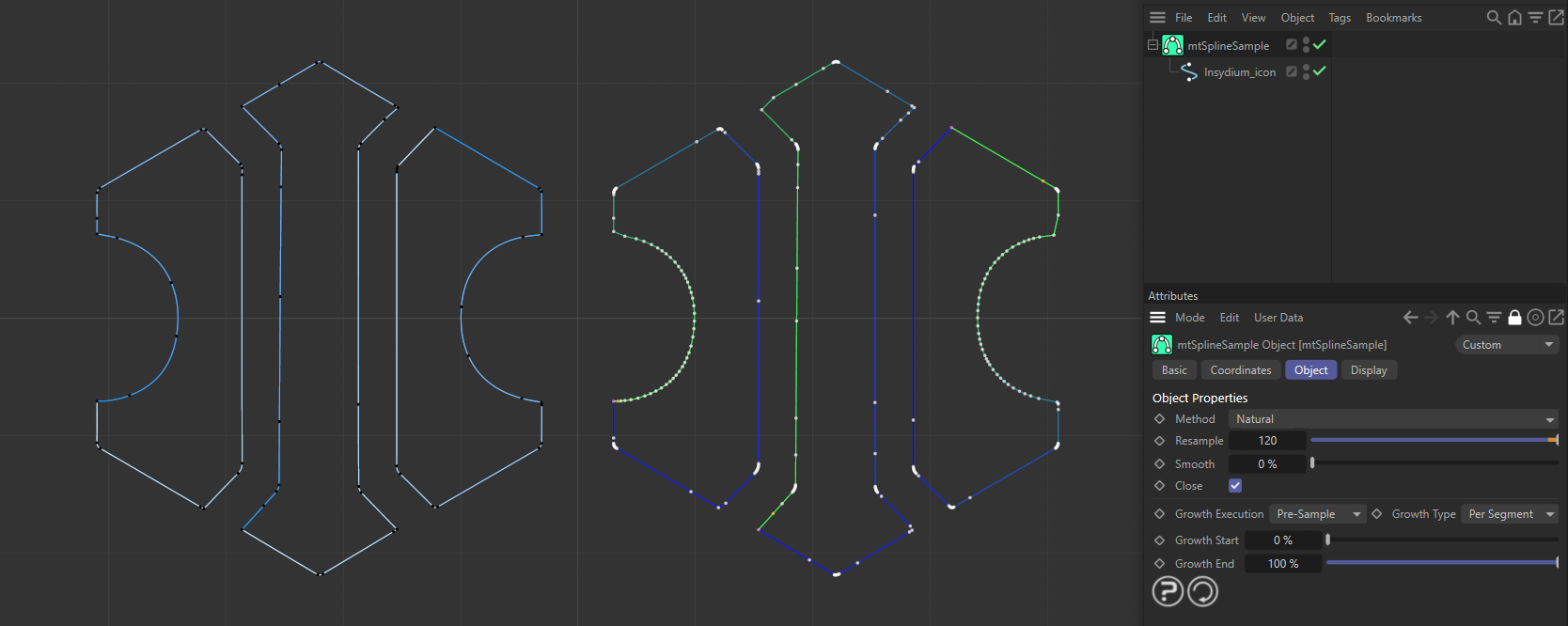
An INSYDIUM logo spline is on the left. On the right, a duplicate spline has been made a child of a mtSplineSample, using the Natural Method.
Resample
Resample can be increased to give you a higher point count per segment.
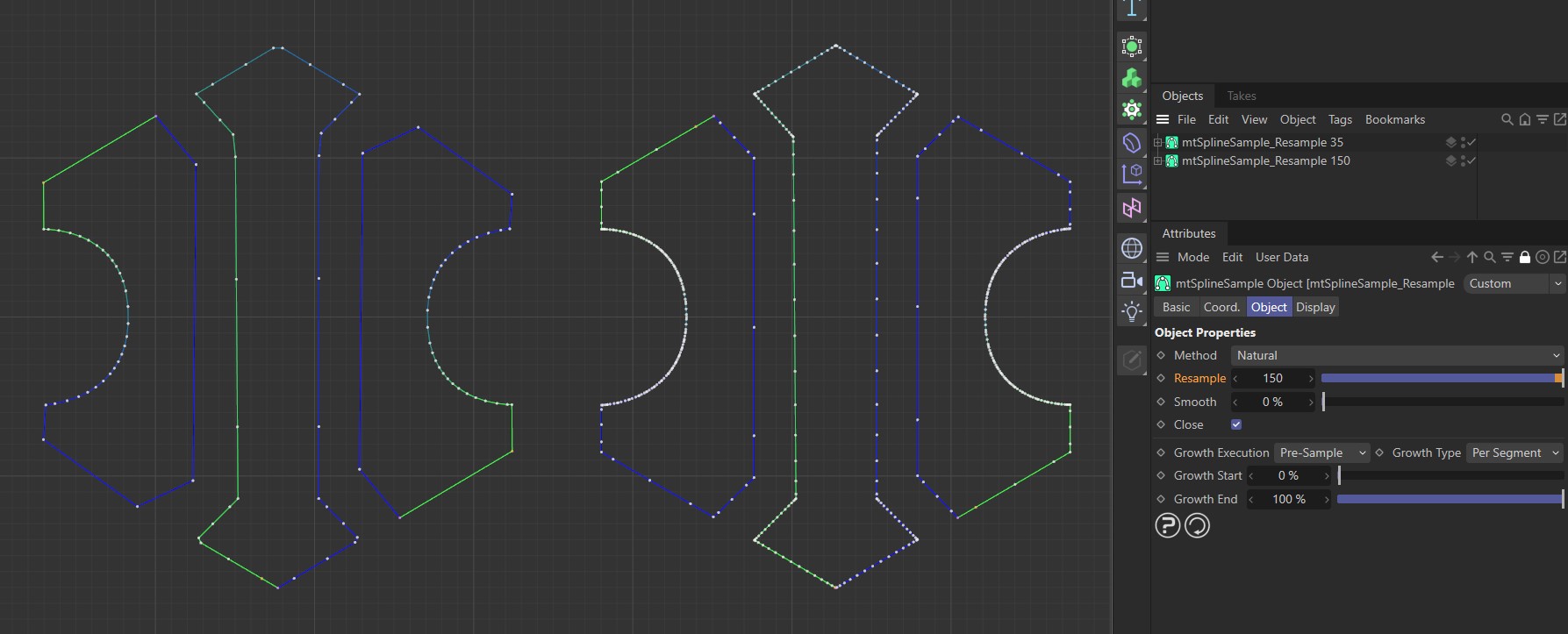
Natural Method, with a Resample setting of 35 points per segment on the left and 150 on the right.
Smooth
Smooths splines on corners, by using the average point - on the segment - between neighboring points.
Distance Method
The Distance Method gives you control over the number of points you require in a set distance.
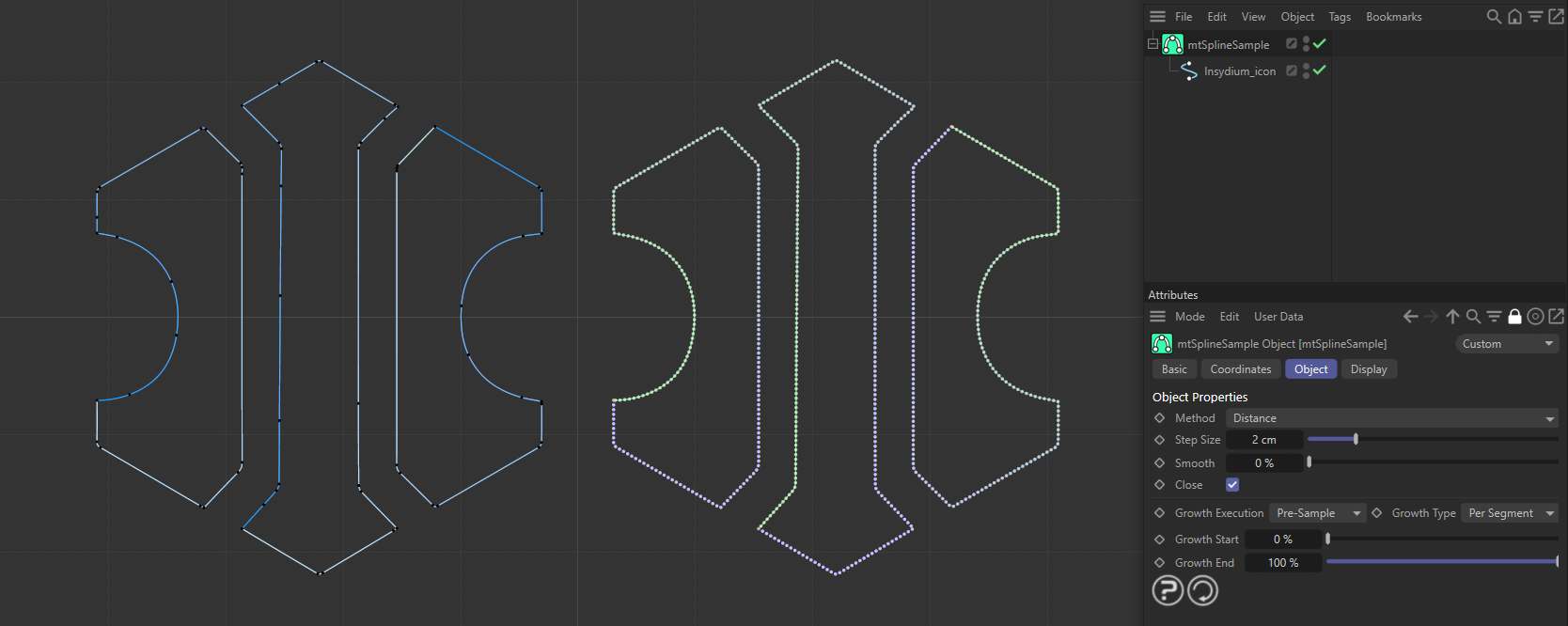
An INSYDIUM logo spline is on the left. On the right, a duplicate spline has been made a child of a mtSplineSample, using the Distance Method.
Step Size
Sets how far apart each point is.
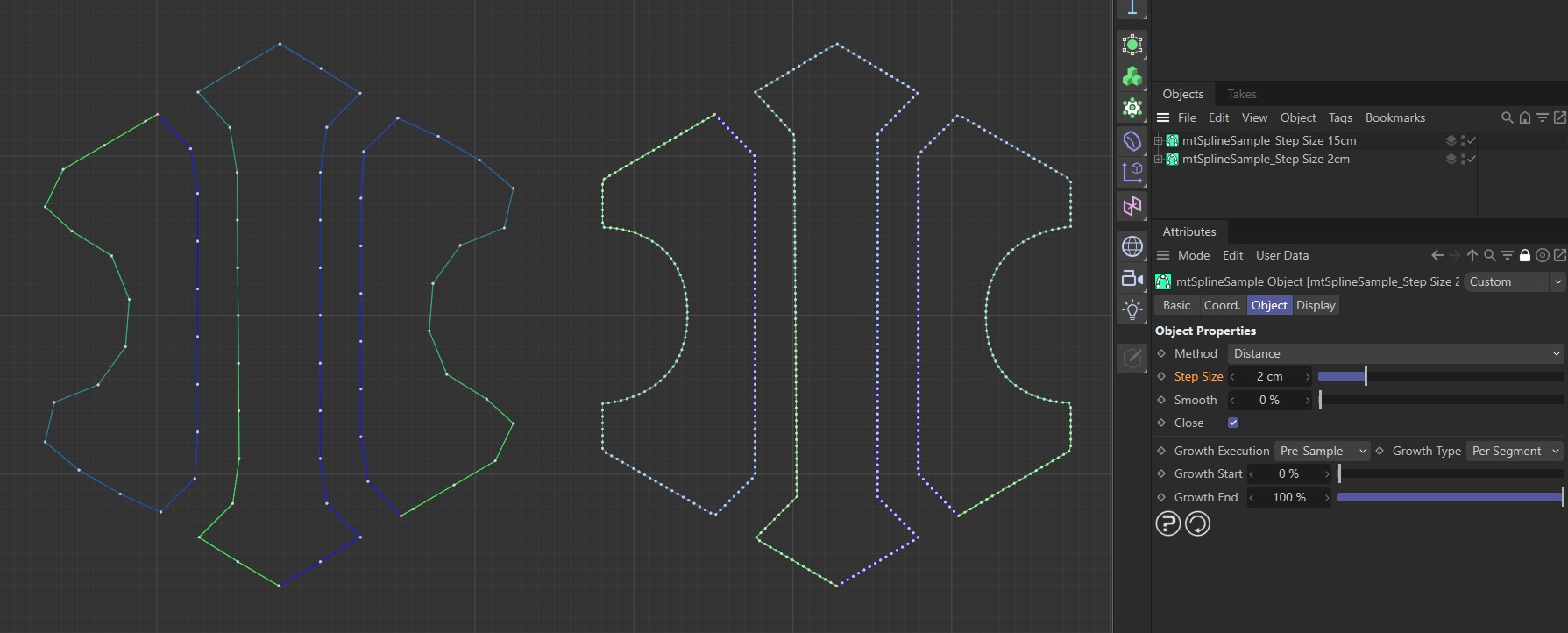
Distance Method with a Step Size of 15cm on the left and 2cm on the right.
Smooth
Smooths splines on corners, by using the average point - on the segment - between neighboring points.
Close
This is disabled as a default. Turning it on will join the start and end points, creating a closed spline.
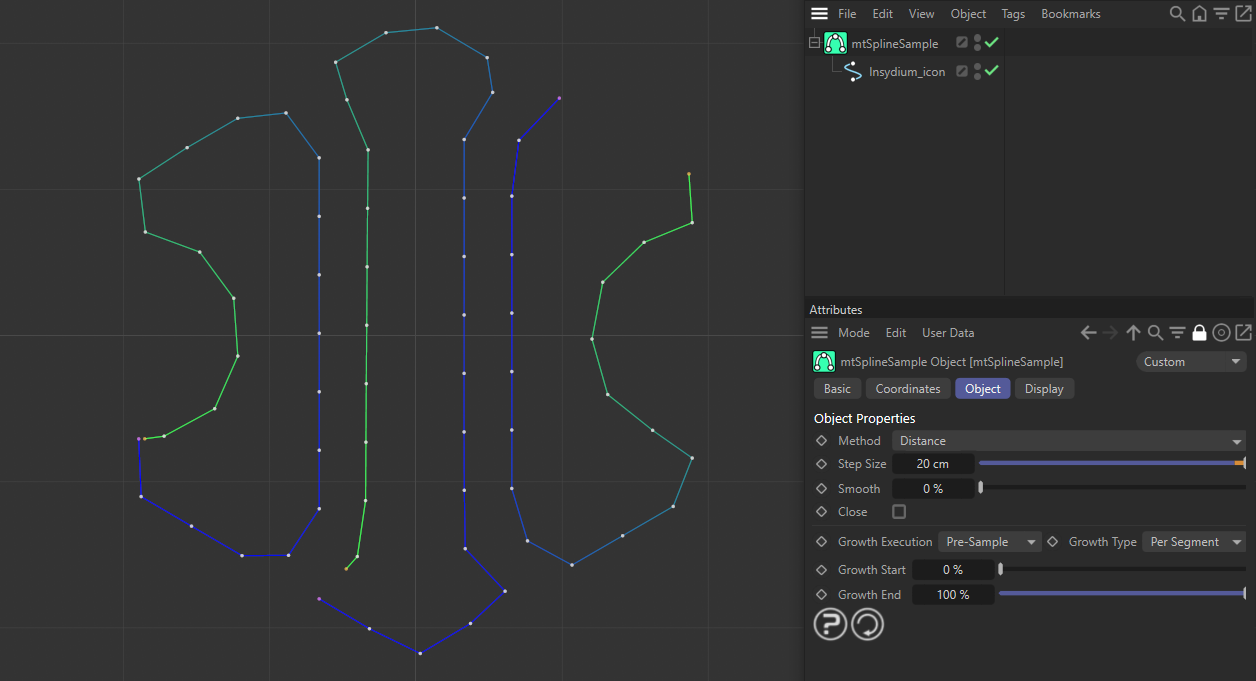
With Close disabled, the start and end points of each segment are not connected.
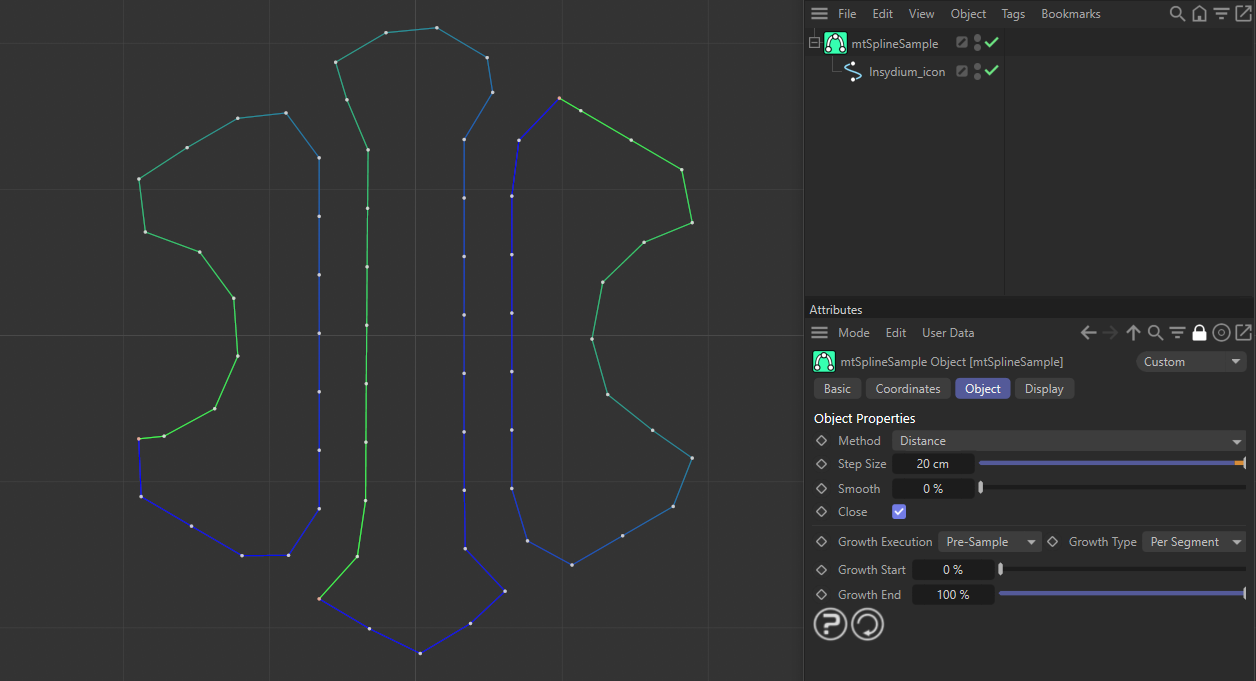
With Close enabled, the start and end points are connected, creating a closed spline.
Growth Execution
The growth settings are for adjusting the start and end points of your spline. They can be animated for growth effects.
There are two settings: Pre-Sample and Post-Sample.
Pre-Sample
Allows you to adjust the start and end points based on the original spline data.
Post-Sample
Allows you to adjust the start and end points using the new spline data
Growth Type
There are two settings: Per Segment and Per Spline.
Per Segment mode
This is the default setting, which controls the growth setting of each segment If the input spline has multiple segments, each segment will have its own start and end point.
Animation demonstrating use of the Growth End slider in Per Segment mode.
Per Spline mode
Per-Spline controls the growth setting of each spline and can begin at either end. The spline will only have one start and end point, even if it contains multiple segments.
Animation demonstrating use of the Growth End slider in Per Spline mode.
Growth Start
The position where the spline starts.
Animation demonstrating use of the Growth Start slider in Per Segment mode.
Growth End
The position where the spline ends.
Note: Growth Start and Growth End can be overlapped.
Display
This tab allows us to change how splines are displayed in the viewpoint.
Display Points
This can be turned off, so that only the start and end points are shown.
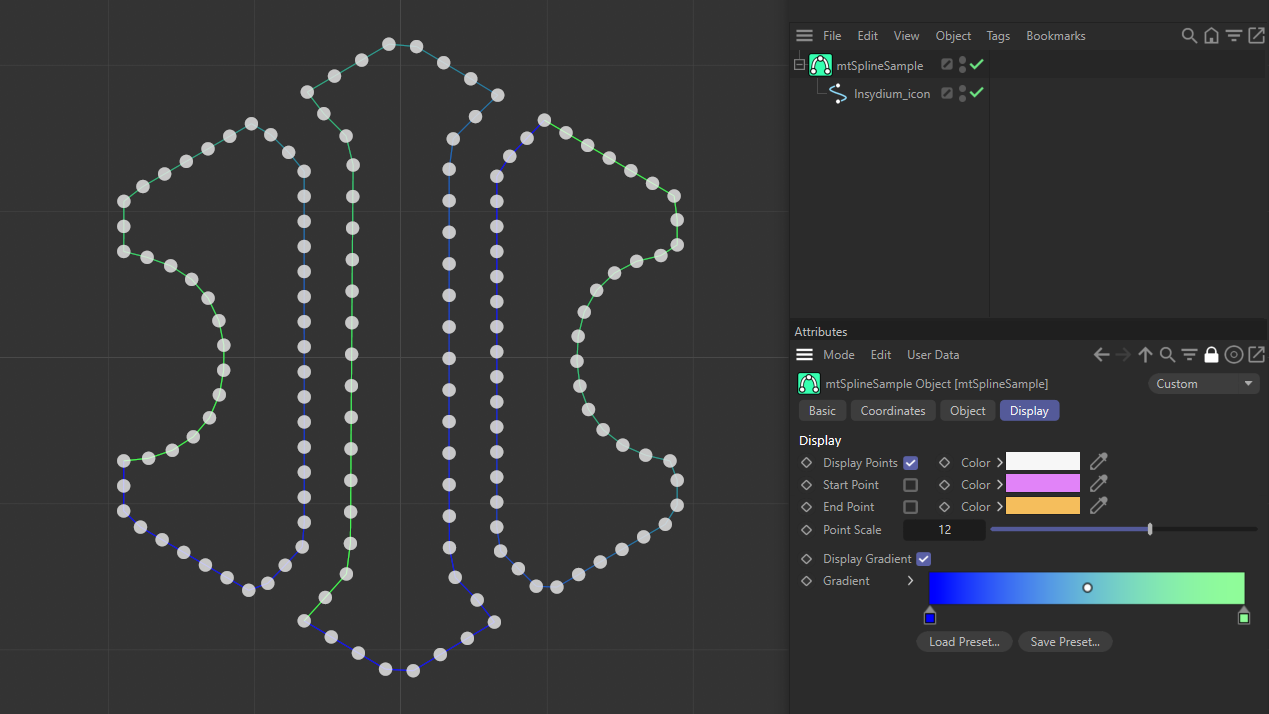
Points shown in white, with Display Points activated.
Start Point
Controls whether the start points are visible.
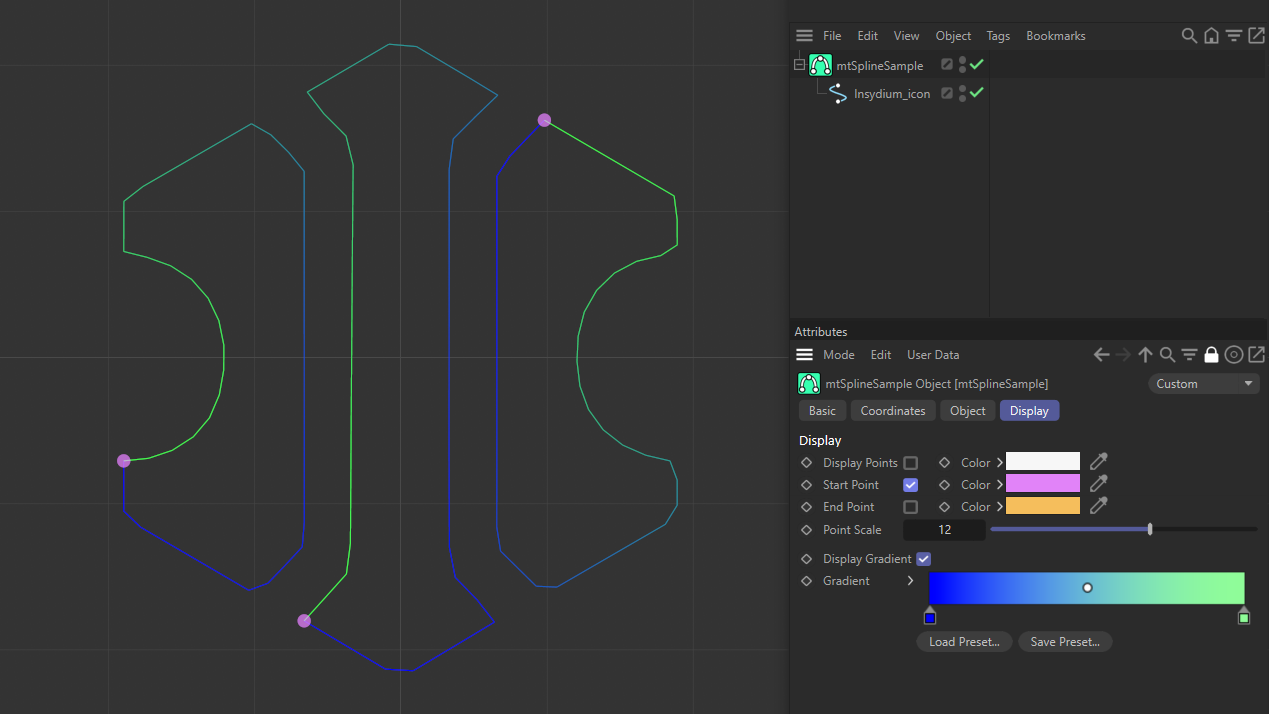
Start points shown in pink, with Start Point activated.
End Point
Controls where the end points are visible.
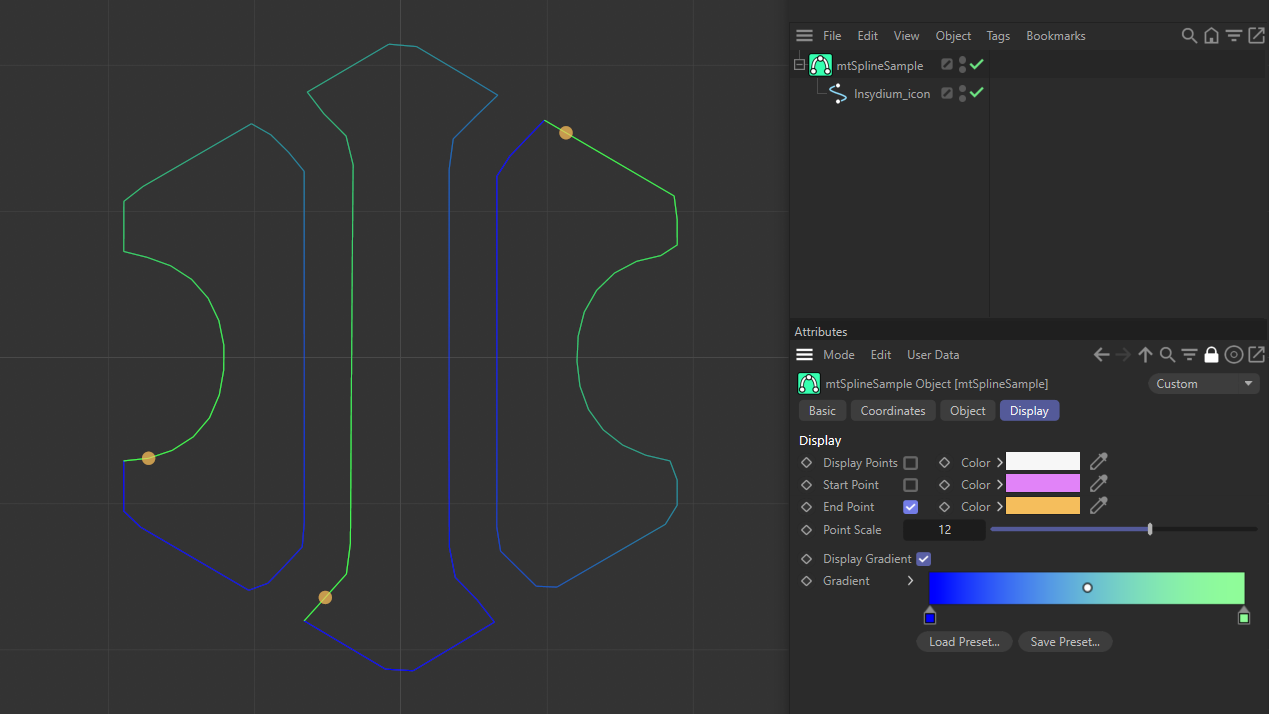
End points shown in yellow, with End Point activated.
Color
You can change the color of the displayed selection using the color picker.
Point Scale
Changes the size of the points.
Display Gradient
Shows the color gradient between the start and end points.
Gradient
This allows you to alter the gradient and the colors used.
Load Preset
You can load a preset gradient from here.
Save Preset
Save any custom preset gradients here.
 mtDualGraph
mtDualGraph mtEdgeSpline
mtEdgeSpline mtInset
mtInset mtPolyScale
mtPolyScale mtSelect
mtSelect mtShellGen
mtShellGen mtShortestPath
mtShortestPath mtSubDivider
mtSubDivider mtRemesh
mtRemesh Global Settings
Global Settings Sphere
Sphere Tree
Tree Koch
Koch Dragon
Dragon Fern
Fern Fibonacci
Fibonacci